
Business nonsense
The Globe is getting warmer. But the only contribution of US businesses is an advertising blitz and political arm twisting to discredit climate science

The Globe is getting warmer. But the only contribution of US businesses is an advertising blitz and political arm twisting to discredit climate science
Bunga took the sukhomajri story forward The first village to follow Sukhomajri's development model was Bunga, just 30 km away in Haryana's Panchkula district (see timeline: Divergent trajectories).

Development in the small farm sector holds the key to a holistic progress in the Asia Pacific countries

Nobody expected farm forestry and exotics to become a major source of firewood

Subsidy amounts and sales figures may not always be indicators of commercial success. After a decade old promotion campaign, only a few Indians own solar cookers and fewer still use them. Is the design, which is incompatible to Indian conditions, t
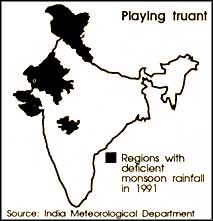
Droughts seem to be here to stay. Wrong development policies, governmental indifference and relief schemes which don't work have led to a situation where a large part of the nation faces scarcity despite a year of almost normal rainfall
Loan waiver for farmers is a good beginning M K Venu A former bureaucrat who had worked with finance minister P Chidambaram in 1997 summed up the 2008-09 Budget aptly in the words of Edmund Burke: "Mere parsimony is not economy. Expenses and great expenses may be an essential part in true economy'. The bureaucrat in question, former revenue secretary N K Singh, had then designed one of the most liberal tax amnesty schemes for the urban rich with a view to mainstreaming sources of black money generation. The amnesty programme had later prompted even the Supreme Court to comment that such schemes must not become regular practice. Those were difficult times when a prolonged growth slump in much of Asia had led to sluggish revenue collections year after year. Budget targets were rarely met, if at all. Consequently, the government had to resort to amnesty schemes, in desperation, to collect more revenues. Things have dramatically changed in recent years. Asia is fast becoming the engine of growth, and India is a big part of the story. The government's revenues have soared from about Rs 2,54,000 crore in 2003-04 to Rs 5,85,000 crore in 2007-08, more than doubling in four years. With its coffers overflowing, the UPA government has chosen to embark on a "great expenses' programme. And why not? If you could give amnesty to the rich in difficult times, why not amnesty to the poor, distressed farmers when the coffers are full up? The Rs 60,000 crore farm loan waiver may have some design flaws, but no one today should quarrel with the sentiment that agriculture, and the small farmer, do need a leg-up. Clearly, the distress in the farm sector in recent years has created an adverse political climate for the UPA, which has been a bit shy of selling more aggressively the unprecedented GDP growth India has seen in the past five years. It is obvious that you cannot sell high GDP growth and bulging forex reserves in large parts of rural India which are in distress. This had also become a cause of persistent friction between the Congress and the Left within the UPA alliance. All this while, it would appear, it is this political tension which had resulted in the growing communication gap between the Congress and the Left. This may have had its spillover effect even on the nuclear deal. The Left would seem to have been somewhat assuaged by the Budget proposals. The CPM general secretary Prakash Karat has for the first time welcomed the farm and social sector programmes announced by the finance minister. This may signal a temporary thaw in the relations between the Congress and CPM. There is talk that the nuclear deal may also get revived, and the Left may not do any more than make some routine noises over it. The larger issue is one of creating a conducive atmosphere in the political economy to build a consensus for further reforms that are critical for India's economy to sustain a 9 per cent growth for the next five years. The massive farm loan waiver and higher spending in social sector programmes must be appropriately used now to bring down the political opposition to further reforms which are important to propel India to the next level in the globalisation sweepstakes. The Budget in some ways has signalled a New Deal, in which every section of society has benefited, whether it's the urban middle class or the rural poor. But these benefits must now be accompanied with some obligation to work towards a common goal. The one common objective, with which the CPM must have no quarrel, is promoting higher levels of industrialisation. The CPM has also formally recorded in its party document that rapid industrialisation is necessary and there is an urgent need to move people from low yield agriculture to industry. Prime Minister Manmohan Singh too has been placing repeated emphasis on this. The only caution that needs to be exercised is this process must be conducted in a democratic, bottom-up fashion. This was the prime lesson of Nandigram and Singur. The farm loan waiver must be seen as a purely temporary relief and there must be some programme by which farm families locked in low-yielding, suboptimal farm activity are moved to non-farm sectors. After one loan waiver, there is no point in their getting into another loan to do unremunerative agriculture. This would be a recipe for future fiscal disasters. Some permanent institutional arrangement must be designed by the Centre and states together to ensure that inherently remunerative farm activity gets a boost with technical, marketing and financial support. The other farm families must be encouraged through new skill development programmes to move to the manufacturing sector. This needs to be done in a focused manner. The Left Front government in West Bengal has designed an elaborate scheme, after the farmer protests in Nandigram, which seeks to handhold farm families for years after their shift to manufacturing townships built on their land. If done democratically, this is the only way to design a long-term solution to the problems of India's farm sector. A rapidly globalising economy just cannot afford 60 per cent of its population in agriculture sharing less than 20 per cent of the national income. This will remain the biggest point of tension in our political economy. The massive farm loan waiver in the Budget only addresses the symptom. Much more needs to be done to address the root cause. The Rs 60,000 crore loan waiver, at least, brings the whole issue to the centre stage. That is clearly a plus.

Water will become the most prized and precious commodity in the coming years. Internecine conflicts over the resource are already the order of the day and a global water crisis seems not too far away. But the water-guzzling US state of California is show
<p><span style="font-size:12px;">Budget 2013-2014: speech of P. Chidambaram, Minister of Finance.</span></p> <p><span style="font-size:12px;"><iframe allowfullscreen="" frameborder="0" height="315" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/3INZf8nHwdY"
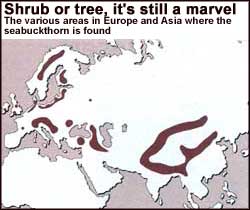
A sturdy mountain tree could transform chilly deserts into lush fields
Support for further economic reforms in the context of India's globalisation will be mustered more easily if the deprived sections are assured of some safety net, says M K Venu FINANCE minister P Chidambaram's fifth budget stumped the chattering classes, mostly with incomes of well over Rs 10 lakh a year. The Rs 10-lakh income threshold is relevant because there are less than 300,000 people in India showing a taxable income of Rs 10 lakh and above. But they exercise disproportionate influence on policy. There are many more in the above income category, who do not pay taxes and probably have even greater influence on public policy! The budget also stumped economists, who are also part of the chattering classes. Initially they did not know what to make of a budget that seemed to give everything to everybody. The budget certainly did not lend itself to instant analysis on television channels where many economic pundits were sitting. In the first flush, one economist simply said he was overwhelmed, and didn't know how the numbers would work after so much goodies were handed out by the finance minister. "I am overwhelmed', is what he kept saying. The impatient TV anchor, obviously looking for a one liner, kept pressing, 'Is it good or bad?'. The only reply was,' I am overwhelmed.' It didn't take long for everyone to realise that it is not necessary for numbers to strictly add up in politics. In certain situations, sentiment and psychology can subsume numbers that don't add up. Which is why politics is often described as the art of the possible. While economics parades as an exact science, there are times when economists get lost in their linear frameworks and miss the wood for the trees. Further, what really stunned the chattering classes was someone like Dr Manmohan Singh or P Chidambaram could come up with such a massive loan waiver package. They associated such acts with politicians like the late Devi Lal, Charan Singh or among contemporaries, Prakash Singh Badal and M Karunanidhi. How could Manmohan Singh and Chidambaram do this, was the main question on their lips. However, at the end of the day the budget seemed to have got overwhelming support, if one went by how the vernacular press treated the finance minister's announcements. Politically, it is one of the sharpest statements one has come across in the past decade and a half. Chidambaram's dream budget in 1997 too had a mesmeric impact on the people but this one covers a much wider terrain in its inclusiveness, whatever critics may carp about. It took a while for the immensity of the political statement to sink into the BJP leaders. Initially some leaders tried to attack the Rs 60,000 loan waiver as irresponsible. Later, possibly after deeper consultations within the BJP leadership, it was decided to tone down the attack. The politics of it was visible even in Parliament when Chidambaram said only kulak landlords will oppose loan waivers for small farmers holding up to two hectares of land. The invocation of kulak landlords has an interesting dimension. Politically, it is significant that the Congress is attempting to wean the poorest among the backward caste, scheduled castes and minorities away from regional parties that have established themselves over the years. This would easily rank as among the most audacious attempts by the Congress to upset the present political arithmetic of various strong regional parties. If viewed in this perspective, it becomes easy to understand why considerations such as fiscal profligacy and misplaced budget assumptions do not stand a chance. In any case, of late, a feeling had developed in non-urban India that the country was reaping the riches of globalisation, in terms of mounting forex reserves, high corporate profits, and government revenues doubling in three years. IN SUCH a situation it becomes difficult to convince the other India that fiscal belt tightening is the way to go. Besides, this would be most hypocritical as even anecdotal evidence would suggest that the bulk of the growing government subsidies today are consumed by the urban middle class. Just take the Rs 71,000-crore energy subsidy. Over 80% of it must be going to the urban middle class. The finance minister has also been careful in not going overboard while opening the purse strings. He has kept enough head-room in his fiscal deficit target to ensure that some discipline remains. For instance, he has budgeted fiscal deficit at 2.5% of GDP, when he could have kept a target of 3% as per the FRBM timeline. He can technically spend extra about 0.5% of GDP or Rs 20,000 crore, without violating the FRBM Act. In fact, the expenditure on loan waiver in the first year could be no more than Rs 20,000 crore. Operationally, the waiver of Rs 60,000 crore will occur over three years. More interestingly, much of the write-offs will happen among loans which are already sitting as non-performing assets (NPAs) in banks. So the bank books will get cleaned up to that extent. In lieu of the write-offs, the banks could receive government bonds which they could liquidate in the market or sell to the Reserve Bank of India. True, this may constitute another offbalance sheet borrowing by the government. Even after taking some of the off-balance sheet items, heavens won't fall if the fiscal deficit moves up to 4% of GDP. What is the great sanctity to the 3% figure, one fails to understand. Both oil and food subsidies today are being enjoyed across the board by urban and rural India, and these subsidies have helped to keep food prices under control. It is difficult to imagine the political class surviving if the price of wheat in India were to track international trend. Global wheat prices have doubled in the past year. The price of other mass consumption items such as edible oil too has been maintained at lower than international price. Bad economics, but good for collective survival. So current circumstances in the global economy are exceptional and the budget has done well to admit that there are off-balance sheet subsidies whose value is growing by the day on account of rising global prices. Finally, support for further economic reforms in the context of India's globalisation will be mustered more easily if the deprived sections are assured of some safety net. The benefit of all this will eventually accrue to the growing aspirational middle class. This perspective must not be lost sight of. After all, it is in the interest of the emerging bourgeoisie to keep the present system alive and ticking.

Dharwad (Karnataka) Opposition to GATT in Karnataka is spearheaded by the Karnataka Rajya Raitha Sangha (KRSS), which has gained strength over the past 2 years and forced the ruling Congress

Biotechnology, which holds the answers to many persistent problems such as controlling disease and increasing food production, has tremendous potential in cash strapped India. But to succeed, it needs a helping hand from industry.
The Kerala government has decided to appeal against two national green tribunal orders that said that the government should take note and adhere to the recommendations of the Western Ghats Expert Ecology Panel (WGEEP) report while approving private and commercial development in eco-sensitive zones. Read more in this September 2013 edition of the Monthly India State of the Environment Report published by the South Asia Environment Portal. Read and Share.

As the reckless plundering of the world"s limited resources continues, nature is striking back where it hurts humans most: disease. People in some places are still paying the price of other people"s progress. So what makes planners think that they have a